nopCommerce
nopCommerce an E-commerce Platform
It is the most popular ASP.NET shopping cart in the world.
nopCommerce is the best open-source eCommerce shopping cart solution. nopCommerce is free, and it is the most popular ASP.NET eCommerce platform. The first nopCommerce version was released in 2008. At that time there were no free and open-source shopping carts that would not impose the limitations on business processes and flow hence the essential goal for nopCommerce was to fix that. The high quality of the product and its constant development led to creating the global nopCommerce community of over 250,000 members. The philosophy of the open-source product allows us to receive the contribution of developers and businesses from around the world. That helps us to grow faster and meet the highest security and technology standards.What is nopCommerce?

What is different about nopCommerce?
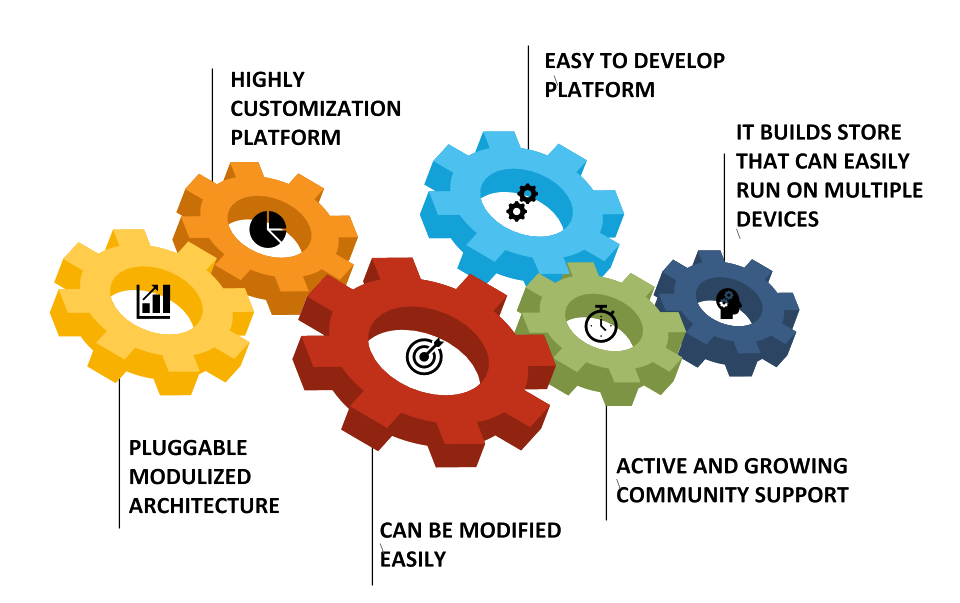
Why to choose nopCommerce for your eCommerce needs?
Having physical shop comes with lots of limitations and responsibilities Have a physical shop and want to sell online please send your query
so for that, we are providing best nopCommerce services
Why to choose nopCommerce
nopCommerce Services we are providing
nopCommerce plugin Development
nopCommerce Maintenance
nopCommerce Templates Designing
nopCommerce Installation
eCommerce Site Development
nopCommerce Customization
A responsive mobile webstore is a must for any online business owner these days, as 82% of smartphone users decide to buy something while surfing the Internet on their smartphones.nopCommerce supports a mobile version of your website with a compelling, feature-rich and graphically pleasing storefront, and it provides means for retailers to immediately deliver relevant offers, promotions and products. The mobile-responsive version works on any connected device.nopCommerce Installation
It is the most popular ASP.NET shopping cart in the world.Start and grow your successful online business with nopCommerce.
In computing, a plug-in (or plugin, add-in, addin, add-on, or add on) is a software component that adds a specific feature to an existing computer program. When a program supports plug-ins, it enables customization. Plugins are a set of components adding specific capabilities to a nopCommerce store You can extend the functionality of nopCommerce by installing and configuring plugins. Plugin include things such as discounts, shipping methods, tax providers, and widgets. Perfect for creating an online store of any size and type nopCommerce offers powerful out-of-the-box features for effective B2C and B2B sales , without any restrictions and absolutely free: Unlimited products, staff accounts and their advanced features Variety of tools for professional marketing and sales growth Popular payment methods and gateways Shipping features Multi-vendor and multi-store functionality Advanced business reporting and analytics High performance and scalability Integrations with all popular third party services GDPR support nopCommerce meets all European Union Laws See our nopCommerce plugins hereWhat is nopCommerce plugin?
What is Plugin?
How nopCommerce plugin will help you?
How to install a plugin in nopCommerce
Why do store owners use nopCommerce?
Checkout our nopCommerce newly built plugins and add more functionality to your store